COMBINE-CT
Combining diagnostic data and interventional approaches for futureproof cardiology care

6 countries
11 participants
November 2023 — October 2027

HORIZON JU Research and Innovation Actions
A European Project to Deliver Futureproof Cardiology Care
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is caused by the pathological process in which fat, cholesterol and calcium accumulate on the arterial wall. It is the leading cause of mortality in the world, affecting in 2019 about 200 million individuals or 2.5% of the global population and resulting in over 9 million deaths annually.
Despite being recommended as the first line diagnostic test, due to its potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs, Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) is massively underexploited.
In COMBINE-CT, we will deliver a fully automated, vendor agnostic CCTA-enabled workflow for stable CAD patients, covering diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up.
Key Concepts
Angiography
It is a medical image of the blood vessels of the body. It is often used to look for a narrowing of the coronary arteries of the heart, which may be the cause for chest pain. This image can be obtained non-invasively using coronary CT angiography, or invasively using coronary catheterization.
Artificial Intelligence
It is the quality of algorithms and machines that display cognitive abilities proper of human intelligence. Nowadays, the term artificial intelligence usually makes reference to machine learning and deep learning.
- Machine Learning is the branch of artificial intelligence that studies computer programs that modify themselves to achieve a goal.
- Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks.
Chest Pain
Pain in the front of the chest is a common symptom of coronary artery disease, which is a life-threatening situation. A patient that arrives with chest pain to the emergency room will undergo diagnostic testing to determine the cause of the chest pain. Testing might start with an electrocardiogram and blood tests, but if results are inconclusive an angiography might also be required to emit a definitive diagnosis.
Computed Tomography (CT)
It is a medical imaging technique that uses a rotating X-ray tube to obtain internal images of the body.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
It is the narrowing of cardiac arteries due to the build-up of atherosclerotic plaque, caused by high cholesterol and other risk factors.
As a consequence, the blood flow to the cardiac muscle is decreased, and angina or myocardial infarction might ensue, which is a life-threatening situation. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw.
Coronary Catheterization
It is a medical invasive procedure to access the coronary arteries of the heart using a catheter. It can be used for diagnostic and treatment purposes.
- Injecting a contrasting agent through the catheter, and using X-ray imaging, this technique reveals the coronary arteries and provides an angiography image.
- Opening a blocked coronary artery and placing a stent to keep it open, this technique is used to treat coronary artery disease.
Although this technique is non-surgical and minimally invasive, it is not free from complications.
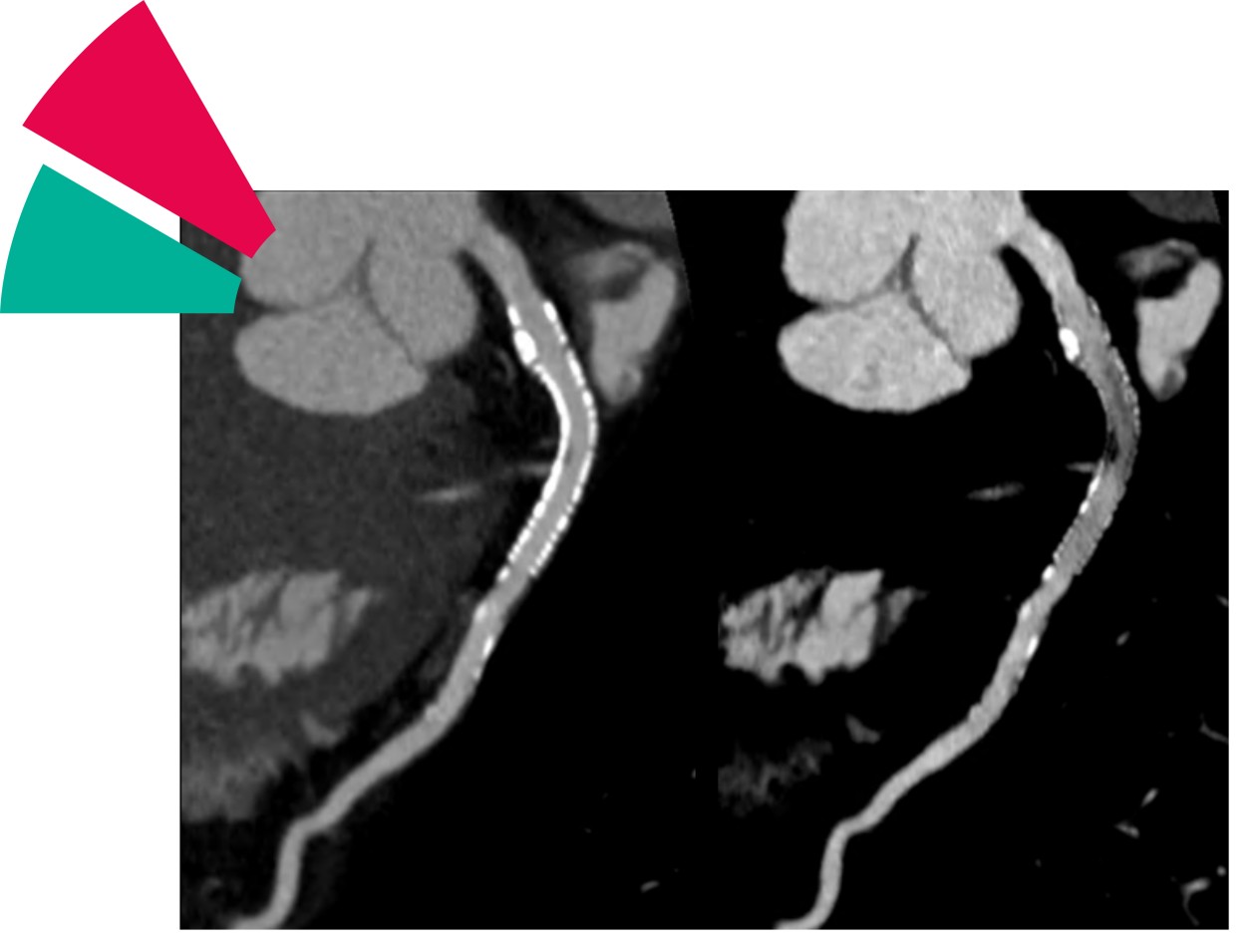
Coronary CT Angiography (CCTA)
It is an angiography image acquired using a CT scan. A contrasting agent must be injected so that blood vessels are visible in the CT image.
Ischemia
It is a reduction in the blood flow to any tissue or organ of the body, that causes a shortage of oxygen and nutrients, with resultant damage or dysfunction.
Spectral CT Scanner
It is new type of CT scanner that is able to differentiate the energy of the X-ray into high energy and low energy. This characteristic improves the resulting images and makes it easier to differentiate body tissues in the images.
Spectral Photon-Counting CT (SPCCT) Scanner
Like the spectral CT scanner, this scanner that is able to differentiate the energy of the X-rays, by measuring the energy of individual photons. This improves further the resolution and characteristics of the image.
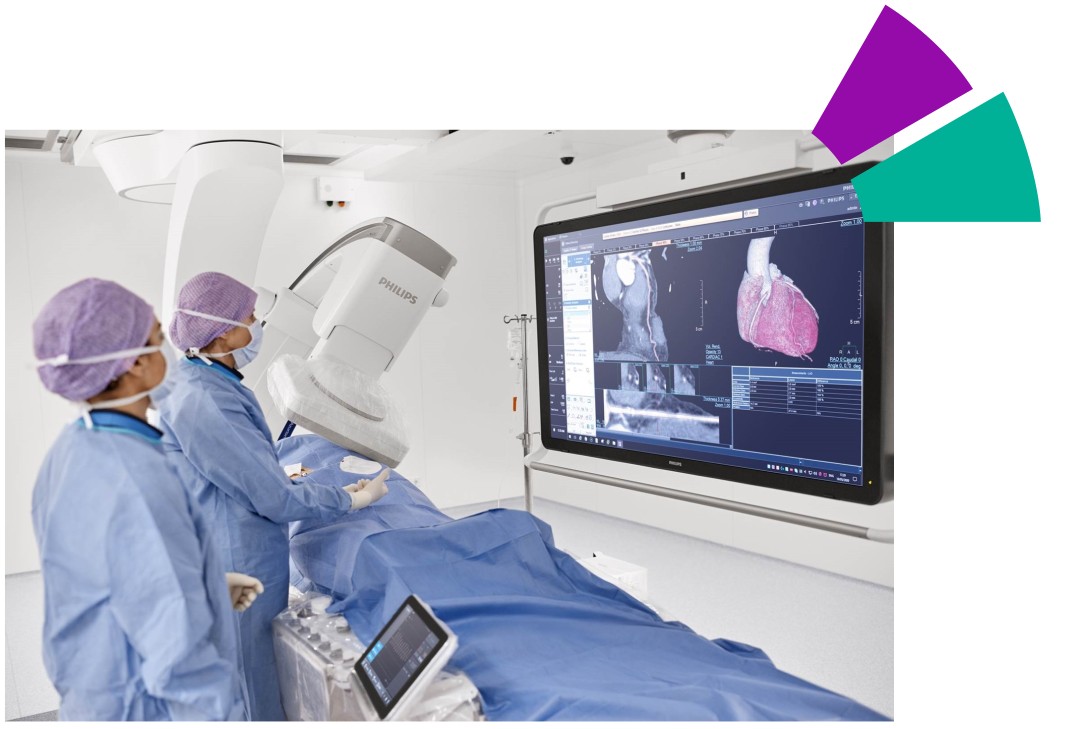
Our Objectives
Our goal is to deliver a fully automated, vendor agnostic CCTA-enabled workflow for stable CAD patients to:
• Offer a definitive ischemia diagnosis
By using spectral information and AI to reduce motion artifacts and enhance the image for accurate coronary assessment, developing patient specific acquisition protocols, adequate risk stratification, all in a vendor agnostic one-stop shop application.
• Improve CAD procedure outcomes
By planning the intervention with CCTA information, seamlessly integrating CCTA data in the catheterization lab, and offering an intuitive multi-modal information fusion.
• Prove its value for patients and hospitals
By offering outstanding clinical evidence of the accuracy and benefits of the CCTA workflow, validating our findings in all types of clinical scenarios, analysing the health economics of deploying this workflow in non-research settings, and engaging patients early in study design.
The Consortium












